Nutritional Content of Cabernet Sauvignon Wine
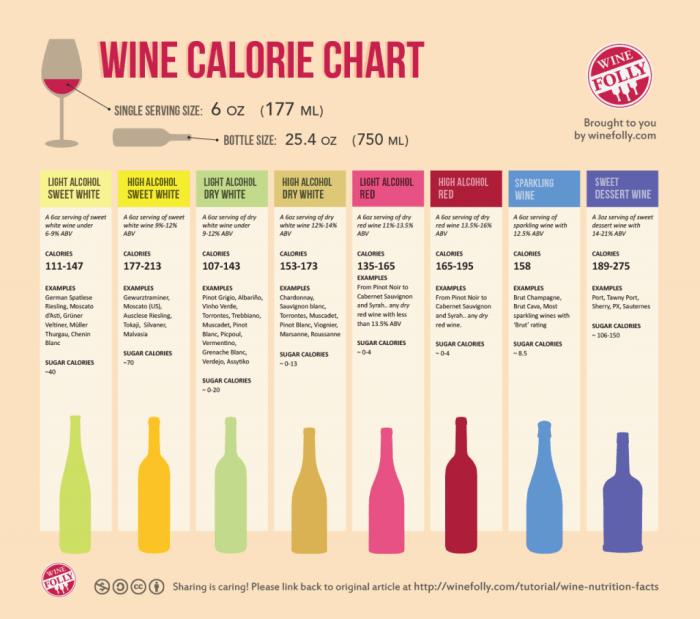
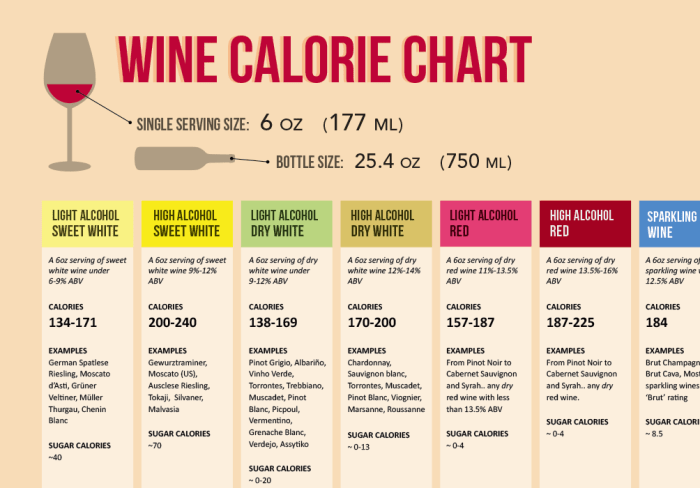
Nutrition facts for cabernet sauvignon – Cabernet Sauvignon, a full-bodied red wine known for its complex flavors and rich aroma, also possesses a unique nutritional profile. While moderate consumption of alcohol is associated with some potential health benefits, it’s crucial to understand the nutritional content of Cabernet Sauvignon and its implications for overall health. This section will delve into the specific nutrients found in a standard serving, comparing it to other alcoholic beverages.
Nutritional Components of Cabernet Sauvignon
A standard 5-ounce serving of Cabernet Sauvignon typically contains a modest number of calories, primarily from alcohol. It also offers small amounts of carbohydrates and negligible amounts of fat and protein. However, the wine’s true nutritional significance lies in its antioxidant content. The following table summarizes the typical nutritional breakdown:
| Nutrient | Amount per 5 oz Serving | % Daily Value (DV)* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 125 | ~6% (based on a 2000 calorie diet) |
| Carbohydrates | 4g | ~1% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Alcohol | 12-14% by volume | N/A |
Daily Value percentages are estimates and may vary depending on individual dietary needs and other factors.
Antioxidants in Cabernet Sauvignon and Their Health Benefits
Cabernet Sauvignon is rich in various polyphenols, a class of antioxidants known for their potential health benefits. These include resveratrol, catechins, and tannins. Resveratrol, in particular, has garnered significant attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective properties. Studies have suggested a link between moderate red wine consumption (containing resveratrol) and a reduced risk of heart disease, although more research is needed to establish a definitive causal relationship.
The exact quantities of these antioxidants vary depending on factors such as grape variety, soil conditions, and winemaking techniques. However, the concentration of these beneficial compounds contributes to Cabernet Sauvignon’s potential role in promoting overall well-being.
While Cabernet Sauvignon’s nutritional profile primarily focuses on its alcohol content and potential antioxidants, it’s interesting to compare its minimal nutritional impact to other seemingly innocuous items. For instance, you might be surprised by the sodium content revealed in the morton salt nutrition facts , highlighting how even seemingly insignificant additions can impact our daily intake. Returning to Cabernet Sauvignon, remember moderation is key when considering its overall nutritional contribution to your diet.
Comparison with Other Alcoholic Beverages, Nutrition facts for cabernet sauvignon
Compared to other alcoholic beverages, Cabernet Sauvignon’s nutritional profile presents some distinctions. Beer, for instance, typically contains more carbohydrates due to the fermentation process using grains. White wines generally possess lower levels of antioxidants compared to red wines due to the absence of grape skins during fermentation, which are a primary source of polyphenols. The calorie content can vary across all types, depending on serving size and alcohol content, but generally, a 5-ounce serving of Cabernet Sauvignon falls within a similar range to a standard serving of other alcoholic beverages.
However, the specific antioxidant profile, notably the higher concentration of polyphenols in red wines like Cabernet Sauvignon, sets it apart.
Health Implications and Considerations: Nutrition Facts For Cabernet Sauvignon
Moderate consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon, like other alcoholic beverages, presents a complex interplay of potential benefits and risks. While some studies suggest possible cardiovascular advantages, it’s crucial to understand the potential downsides and individual sensitivities before incorporating it into one’s lifestyle. The key lies in responsible consumption, recognizing personal limitations and potential health interactions.Cabernet Sauvignon, like other alcoholic beverages, contains ethanol, which is the primary active ingredient responsible for its effects.
The body metabolizes ethanol, and excessive consumption can lead to a range of negative health consequences. Conversely, moderate intake has been associated with certain potential health benefits, primarily related to cardiovascular health, although more research is needed to fully understand these relationships. It is important to note that these potential benefits are only realized within the context of moderate consumption and a healthy lifestyle.
Potential Health Benefits and Risks of Moderate Cabernet Sauvignon Consumption
Moderate consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon has been linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease in some studies. This is potentially attributed to the presence of antioxidants like resveratrol, found in grape skins. However, it’s crucial to remember that these potential benefits are significantly outweighed by the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Heavy drinking increases the risk of liver disease, certain cancers, and other health problems.
The potential benefits are thus contingent upon maintaining a moderate intake level, and should not be interpreted as a license for excessive alcohol consumption. Further, the health benefits, if any, are likely to be marginal compared to the benefits of a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Interactions Between Cabernet Sauvignon and Medications or Health Conditions
Cabernet Sauvignon can interact negatively with certain medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver. For example, individuals taking medications for heart conditions, blood thinners, or those with liver disease should exercise extreme caution and ideally consult their physician before consuming any alcohol, including Cabernet Sauvignon. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing conditions like diabetes or hypertension should be mindful of alcohol’s potential impact on blood sugar and blood pressure levels.
The presence of sulfites in wine may also trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. Always prioritize consulting a healthcare professional if you have any concerns regarding potential drug interactions or pre-existing health conditions.
Defining Moderate Consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon
Moderate alcohol consumption is generally defined as up to one standard drink per day for women and up to two standard drinks per day for men. A standard drink of wine is typically considered to be 5 ounces (148 ml), although this can vary slightly depending on the alcohol content of the wine. It’s crucial to note that this is a guideline, and individual tolerance and sensitivity to alcohol can vary greatly.
Factors such as body weight, metabolism, and overall health significantly influence how the body processes alcohol. Exceeding these guidelines increases the likelihood of experiencing negative health consequences. Regularly exceeding the recommended limits can have detrimental effects on various organs, and should be avoided.
Recommendations for Responsible Cabernet Sauvignon Consumption
The following recommendations emphasize responsible consumption to minimize potential risks:
- Always consume alcohol in moderation, adhering to the recommended guidelines.
- Never drink and drive; designate a driver or utilize alternative transportation.
- Avoid consuming alcohol if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or operating machinery.
- Be mindful of potential interactions with medications or pre-existing health conditions; consult your doctor if necessary.
- Pace your drinking and alternate alcoholic beverages with water or non-alcoholic drinks.
- Be aware of your limits and avoid exceeding your personal tolerance level.
- Consume alcohol responsibly within a balanced lifestyle that incorporates a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
FAQs
Does Cabernet Sauvignon contain carbohydrates?
Yes, Cabernet Sauvignon contains a small amount of carbohydrates, primarily from residual sugars left after fermentation.
Is Cabernet Sauvignon good for heart health?
Moderate consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon, like other red wines, may offer some cardiovascular benefits due to its antioxidants, but this should be considered alongside other lifestyle factors and individual health conditions.
How many calories are in a glass of Cabernet Sauvignon?
The calorie count varies depending on the serving size and alcohol content, but a typical 5-ounce glass contains approximately 125 calories.
Can Cabernet Sauvignon interact with medications?
Yes, alcohol can interact with certain medications. It’s essential to consult a doctor or pharmacist if you have concerns about potential interactions with your prescription or over-the-counter medications.
